Introductory description of the concept/tool
i.e., what it is and why it is important

Agile Development refers to the project management approach of developing increments of software in frequent iterations based on evolving requirements. Agile is an umbrella term for several project methodologies, Scrum being the most widely used.
The concept of Agile was born in 2001 by a team of independent software developers who challenged the traditional, top-down management, waterfall method of completing software development. Originally referred to as lightweight software development methodologies, the developers adopted the term Agile to reflect its lithe, lean style of project management, characterized by frequent iterations.
The technical or specific information or material related to this concept or tool. Developers had produced the Agile Manifesto, which included four values and 12 principles for Agile software development.
Share:
Values
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
12 Principles
- Our highest priority is to satisfy the customer through early and continuous delivery of valuable software.
- Welcome changing requirements, even late in development. Agile processes harness change for the customer’s competitive advantage.
- Deliver working software frequently, from a couple of weeks to a couple of months, with a preference to the shorter timescale.
- Businesspeople and developers must work together daily throughout the project.
- Build projects around motivated individuals. Give them the environment and support they need and trust them to get the job done.
- The most efficient and effective method of conveying information to and within a development team is face-to-face conversation.
- Working software is the primary measure of progress.
- Agile processes promote sustainable development. The sponsors, developers, and users should be able to maintain a constant pace indefinitely.
- Continuous attention to technical excellence and good design enhances agility.
- Simplicity (the art of maximizing the amount of work not done) is essential.
- The best architectures, requirements, and designs emerge from self-organizing teams.
- At regular intervals, the team reflects on how to become more effective, then tunes and adjusts its behavior accordingly.
How Its Used
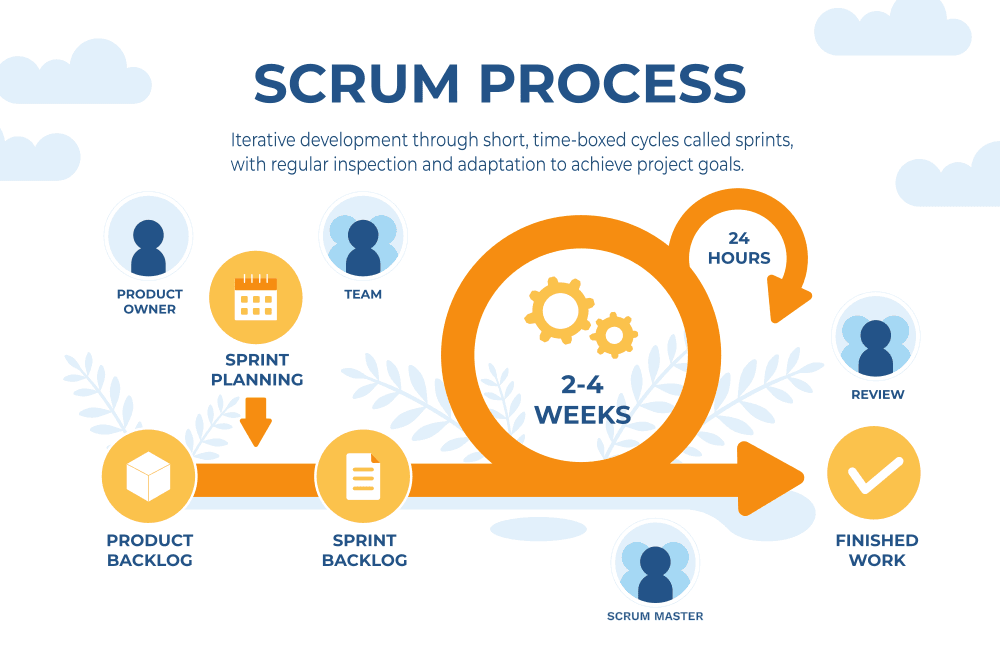
Self-organized, cross-functional development teams work in close collaboration with the customer and stakeholders to add value to every step of the process, targeting a goal of continuous improvement. Agile project management has evolved into a number of project styles, Scrum and Kandan being the most widely used.
In Agile, the team is always working highest-priority items within the sprint timebox, ensuring that the customer receives the right product to meet their requirements.
Benefits
- Provides flexibility in development evolution—small changes can be made easily.
- Allows for early and regular releases.
- Reduces costs.
- Reduces waste of resources.
- Reduces risk—issues are discovered and resolved early.
- Encourages involvement of product owners, development team, and stakeholders.
- Encourages team ownership.
- Eliminates the need for long specification documentation.
- Increases customer satisfaction.
- Increases team performance, communication, and motivation.
