Milestones for Successful Venture Planning
Design thinking is a process that entails solving complex problems with a focus on the “human” element. It enables us to tap into thoughts, and abilities that are not apparent in traditional problem-solving – “Creative Juices”. The goal of design thinking is to combine emotional, functional, process innovation to create viable, feasible, and desirable solutions through iteration.

Share:

What is design thinking and why is it important?
Design thinking allows participants to think outside the box (diverge before you converge) and create alignment and better understanding between team members. This is achieved through a core focus of empathy which enables a user-centred approach to challenges to improve connection and solve the right problems
Design Thinking Consists of the following four iterative stages:
Empathize: The first step in design thinking is to empathize with your customers and stakeholders. This involves understanding their needs, wants, and pain points. To launch a new product, you need to understand what your customers are looking for in terms of features, pricing, and usability. To acquire new customers and retain existing ones, you need to understand their preferences and behaviours. To manage cash flows, you need to understand the financial needs of your business and the concerns of your investors. To ensure that your product or service offering is current, you need to understand market trends and customer feedback.
Define: The next step is to define the problem statement based on the insights gathered in the empathy stage. For example, if you’re launching a new product, your problem statement could be “How might we create a product that meets the needs of our target customers while staying within budget?” If you’re acquiring new customers, your problem statement could be “How might we attract new customers while retaining our existing ones?” If you’re managing cash flows, your problem statement could be “How might we maintain a positive cash flow while investing in new products and services?” If you’re ensuring your product or service offering is current, your problem statement could be “How might we keep our product or service offering relevant in a rapidly changing market?”
Ideate: The ideation stage involves generating as many ideas as possible to solve the problem statement. This is a brainstorming session where you can use techniques like mind mapping, brainstorming, and prototyping. For example, to launch a new product, you could ideate on the features that are most important to your target customers and come up with innovative ways to incorporate those features. To acquire new customers and retain existing ones, you could ideate on marketing campaigns that appeal to both groups. To manage cash flows, you could ideate on cost-saving measures, such as streamlining operations or negotiating better deals with suppliers. To ensure your product or service offering is current, you could ideate on ways to incorporate new technology or improve customer experience.
Prototype: The next stage is to create a prototype of the best ideas generated in the ideation stage. This can be a rough sketch, a digital mock-up, or a physical prototype. The goal is to get feedback from customers and stakeholders to refine the solution further.
Frameworks of design thinking
Different types of frameworks and phases can be used in design thinking. A well-known framework is the Double-Diamond framework (see Figure 1) [4]. This approach which consists of the following phases: Discover, Define, Develop and Deliver. These phases either allow the diverging or converging of ideas.
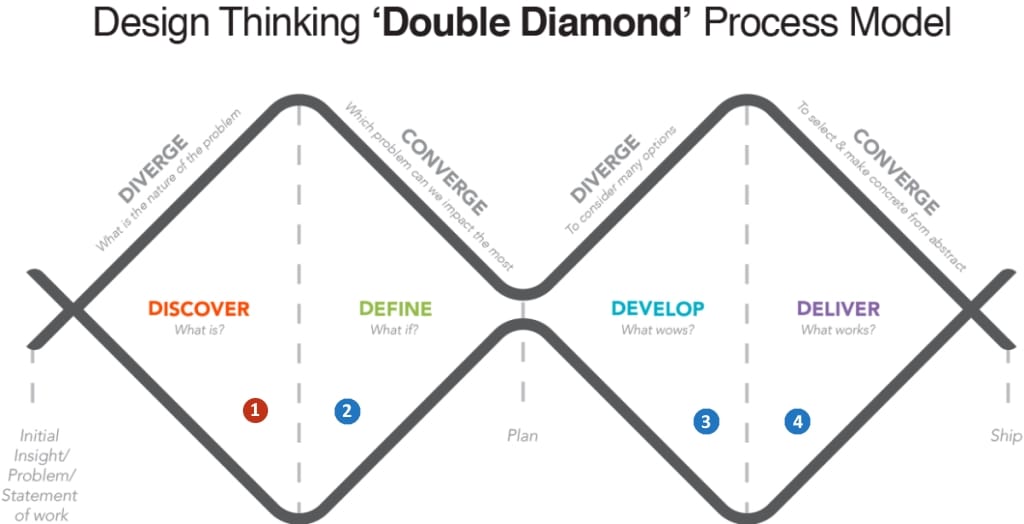
Other well-known phases of design thinking follow the phases of 1) Empathise 2) Define 3) Ideate 4) Prototype and 5) Test [1,3]. These phases are particular useful in product development applications.
Practical techniques and exercises
Practical exercises can guide participants through design thinking frameworks (see templates on Miro). According to A&J Smart, these can be categorized into collect, choose, create, and commit (4 C’s). You can make your workshop by using exercises from the 4 C’s and integrating them with the framework you want. Design thinking is a creative process, and it can be constructed by selecting the various frameworks and exercises required to achieve the overall workshop purpose.
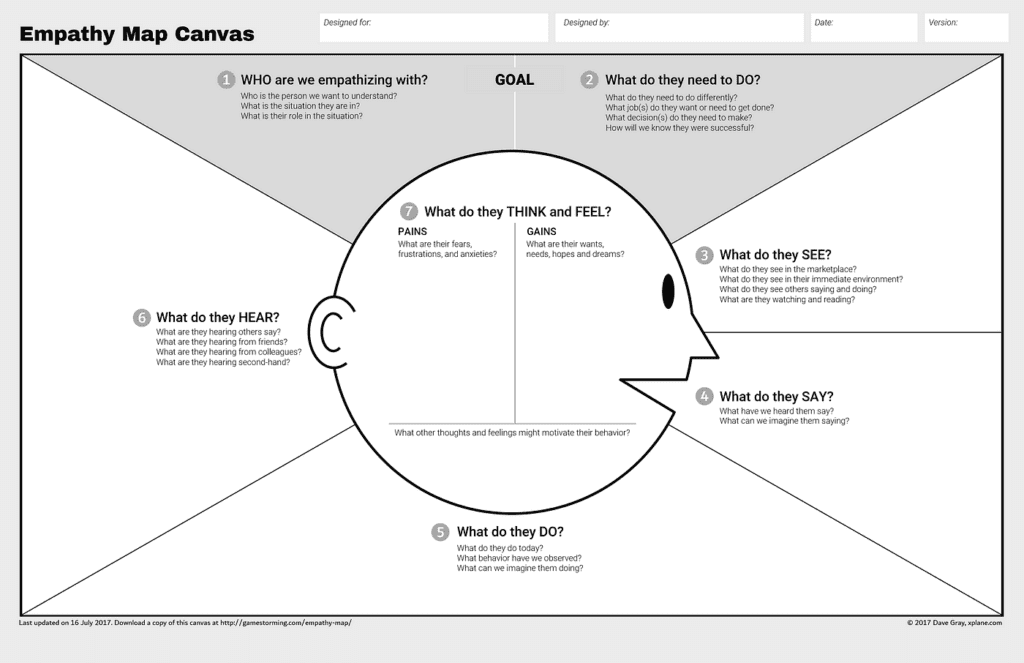
Empathy Map: An empathy map is a tool used in design thinking to help understand the needs and perspectives of users or customers. It is a visual representation of the thoughts, feelings, behaviors, and values of a specific user or customer persona.
An empathy map is typically divided into four quadrants:
Say: This quadrant represents what the user or customer says, such as quotes or feedback about a particular product or service.
Think: This quadrant represents the user or customer’s thoughts, such as their goals, fears, or aspirations related to the product or service.
Do: This quadrant represents the user or customer’s actions, such as their behaviors or actions related to the product or service.
Feel: This quadrant represents the user or customer’s emotions or feelings, such as their frustrations, motivations, or satisfaction related to the product or service.
By filling out the empathy map with information about the user or customer persona, designers can gain a deeper understanding of their needs and experiences. This information can then be used to design products or services that better meet their needs and solve their problems
How to conduct
- Approximately: 25 min at the end of a workshop/ between session
- Using the map below allow participants to add sticky notes to help Visualization of users’ attitudes and behaviours
Parking lot: Parking lot design thinking refers to the application of the design thinking process to the development of parking lot solutions. Design thinking is a problem-solving approach that emphasizes user-centered design, creativity, and innovation. When applied to parking lot design, this approach involves identifying the needs and pain points of users, such as drivers, pedestrians, and property owners, and creating solutions that address these needs in a user-friendly, efficient, and sustainable manner.
The process typically involves several stages, including: Empathizing with users to understand their needs and perspectives, Defining the problem and identifying key design criteria, Ideating potential solutions and creating prototypes, Testing and iterating on the prototypes based on feedback from users and, Implementing the final solution and monitoring its effectiveness.
How to conduct
- Approximately: 5-10 min at the end of a workshop/ between sessions
- Create a black space/box/piece of paper with the work “Parking Lot” on top
- Before the workshop begins tell participants this is where they can add questions, issues or ideas on sticky notes thought-out the workshop
- Discuss the sticky notes at the end of the workshop.
Creative matrix: A creative matrix, in the context of design thinking, is a tool used to organize and generate ideas for a given problem or challenge. It involves creating a grid or table that maps different dimensions or variables of the problem or challenge and then brainstorming ideas at the intersection of these variables.
The creative matrix design thinking approach encourages cross-functional collaboration and encourages the exploration of new ideas and solutions by breaking down complex challenges into manageable components. By considering multiple dimensions and exploring their intersections, the creative matrix can help teams generate new ideas and approaches that might not have been considered otherwise.
How to conduct
- Approximately: 15-20 min
- Create a matrix with rows representing enablers i.e. technology, partnerships, (categories or components of your business-related to your customer [5])
- The column represents consumer segments, user types, actors or personas. Alternatively the columns can be used as a representation of a “How might we”
“Other practical exercises in this category: Expert Interviews, Lighting demos, Product map, Business Model Canvas, Setting the scene, User observations, Retrospective and Sailboat.”
Parking lot: Dot voting is a technique commonly used in design thinking to help teams prioritize ideas and make decisions. It involves giving each team member a set number of dot stickers (usually 3-5) which they can use to vote on their preferred ideas or solutions.
The team members place their dots on the ideas or solutions that they think are the most promising, useful, or relevant to the problem at hand. The ideas with the most dots are then selected for further development or implementation.
Dot voting is a simple and effective way to gather input from multiple team members and facilitate group decision-making. It allows everyone to have an equal say in the decision-making process, and can help to build consensus and agreement within the team.
How to conduct
- Approximately: 5-10 min (usually after an ideation exercise to narrow the selection down.
- Tell participants that they each have a certain number of votes/dots (circles on Miro). You can decide the appropriate number based on the number of participants and how many solutions you want to have at the end of the exercise
- Participants can vote on their own ideas.
- Participants can vote on their own ideas.
- Voting happens in silence without discussion.
Create – Idea Storm (10 for 10): A 10 for 10 idea storm is a design thinking exercise that involves generating 10 ideas in 10 minutes to address a particular problem or challenge. This exercise is designed to encourage rapid ideation, divergent thinking, and collaboration among team members.
To conduct a 10 for 10 idea storm, a facilitator would first present a problem or challenge to the group. The group would then be given 10 minutes to individually generate 10 ideas related to the problem or challenge. The facilitator would then ask each member to share their ideas with the group, one at a time, while other team members listen and build on the ideas presented.
During the idea-sharing process, the group should avoid criticism or judgment of ideas and instead focus on building and expanding on the ideas presented. Once all ideas have been shared, the group can then evaluate and select the most promising ideas to further develop and implement.
The 10 10 idea storm is a simple yet powerful tool for promoting creativity and innovation in a team setting and can be used in a variety of contexts, including product design, marketing, and business strategy.
How to conduct
- Approximately: 8 min (usually after an ideation exercise to narrow the selection down
- This exercise focuses on quantity not quality.
- Tell participants that they will have 1 min to write down an idea on a sticky note. After the 1 minute they will move on to the next sticky note. Do this for 8 minutes.
- Inform participants when the 1 min is up
User Test Flow :In design thinking, a user test flow is a process that is used to gather feedback from users on a product or service. It typically involves the following steps:
Define the goals: Identify the specific goals of the user test, such as identifying user needs, evaluating user experience, or testing usability.
Recruit participants: Identify the target user group and recruit participants who represent that group.
Create test scenarios: Create realistic scenarios that the users will encounter while using the product or service. These scenarios should be designed to test the goals identified in step one.
Conduct the test: Ask the participants to perform the scenarios and observe their behavior. Ask open-ended questions to gather feedback and insights.
Analyze the results: Analyze the data collected during the test to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement.
Iterate and refine: Use the insights gained from the user test to iterate and refine the product or service. Incorporate the feedback into the design and re-test to evaluate the effectiveness of the changes made.
How to conduct
- Approximately: 5-10 min
- Tell participants that they will create sequence of important steps from a starting to end point through the perspective of a hypothetical user.
- Tell participants that they will have 1 min to write down an idea on a sticky note. After the 1 minute they will move on to the next sticky note. Do this for 8 minutes.
- Inform participants when the 1 min is up
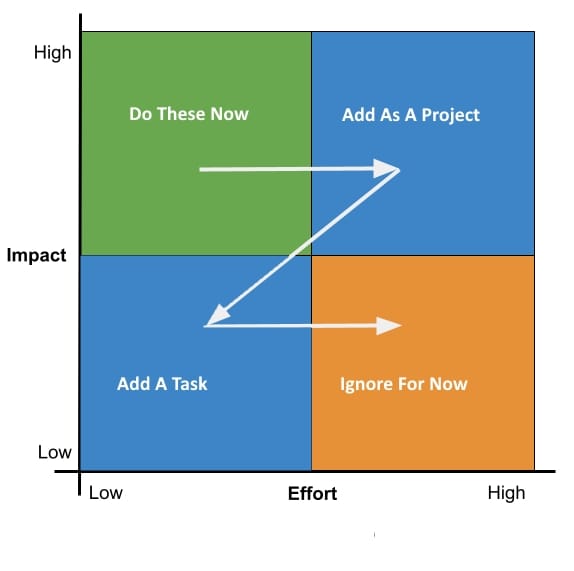
User Test Flow: An effort impact scale is a tool used in design thinking to evaluate and prioritize design solutions based on their potential impact and the amount of effort required to implement them. The scale typically consists of two axes, one representing the level of effort required and the other representing the level of impact or benefit the solution would provide.
The effort axis typically ranges from low to high, and represents the amount of time, resources, and expertise required to implement the solution. The impact axis typically ranges from low to high as well, and represents the potential benefit or value that the solution would provide to the end user or stakeholder.
By plotting design solutions on this scale, teams can identify solutions that offer the greatest potential impact for the least amount of effort, and prioritize those solutions for further development and implementation. This approach can help teams to focus their efforts on solutions that are both feasible and valuable, and avoid wasting resources on solutions that are either too complex or not impactful enough to justify the investment.
How to conduct
- Approximately: 15 min (usually after an ideation exercise to narrow the selection down)
- Ask participants to prioritise each idea my placing the “idea/sticky note” on the graph. Move the sticky note to the correct place through facilitating the discussion of the level of impact and effort required by the idea given.
- Once all ideas are placed, determine which ideas are of high impact, and little effort.
- Note: Effort refers to the amount of effort required by the team/participants to implement an idea
“Other practical exercises in this category: Note taking, doodling, Crazy eights, three Step Concept, Quick Ideas, Business Strategy Concept, Elevator Pitches, SCAMPER”
Effort Impact Scale:An effort impact scale is a tool used in design thinking to evaluate and prioritize design solutions based on their potential impact and the amount of effort required to implement them. The scale typically consists of two axes, one representing the level of effort required and the other representing the level of impact or benefit the solution would provide.
The effort axis typically ranges from low to high, and represents the amount of time, resources, and expertise required to implement the solution. The impact axis typically ranges from low to high as well and represents the potential benefit or value that the solution would provide to the end-user or stakeholder.
By plotting design solutions on this scale, teams can identify solutions that offer the greatest potential impact for the least amount of effort, and prioritize those solutions for further development and implementation. This approach can help teams to focus their efforts on solutions that are both feasible and valuable, and avoid wasting resources on solutions that are either too complex or not impactful enough to justify the investment.
How to conduct
- Approximately: 15 min (usually after an ideation exercise to narrow the selection down)
- Ask participants to prioritise each idea my placing the “idea/sticky note” on the graph. Move the sticky note to the correct place through facilitating the discussion of the level of impact and effort required by the idea given.
- Once all ideas are placed, determine which ideas are of high impact, and little effort.
- Note: Effort refers to the amount of effort required by the team/participants to implement an idea
“Other names of practical exercises in this category: 2-Year Goal, Can We Questions, Define the Purpose, Storyboarding, Breadboarding, Roadmap, Divide and Conquer, Turn Ideas into Actions.”
Applications to programme and product management
Comprehensive program planning: A typical step in programme scoping is conducting a needs assessment to determine the current situation and identify any gaps that the program will need to address. Empathy maps are an example of a practical exercise that can help identify an organization’s needs, problems and purpose.
Risk identification & mitigation: Idea storms (10 for 10) are an example of a practical exercise within design thinking that could be used to identify multiple risks to a programme or project. A similar approach could be used to brainstorm responses or mitigations to risks. This exercise focuses on collecting large quantities of ideas, rather than the best quality. This ensures multiple ideas and perspectives can be integrated.
Scenario planning: User story mapping is an example of an exercise that can be used to generate an expected path or sequence of events. This can represent the risks and responses that follow a path of a scenario as it might occur in programme management. For example, you could ask participants to start with the same/different key drivers of a scenario and create a sequence of events (sticky notes) as they would expect them to occur. After this exercise, it might be useful to create an overall group mapping of the single or multiple scenarios generated.
Design Thinking is more than just a problem-solving tool; it’s a mindset that fosters innovation, creativity, and user-centered solutions. By embracing empathy, experimentation, and collaboration, organizations and individuals can uncover insights that lead to truly impactful designs. The iterative nature of Design Thinking ensures that solutions are continually refined and improved, keeping the user at the heart of every decision. In a rapidly evolving world, the ability to think creatively and adapt to new challenges is invaluable, and Design Thinking offers a robust framework to navigate this complexity, ultimately leading to meaningful and sustainable innovation.
